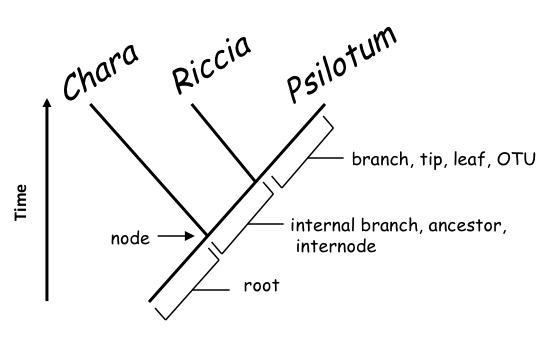
FIGURE 2. Figure 2. A rooted phylogenetic tree, showing relationships among three taxa Chara, Riccia and Psilotum. The tree consists of branches (representing species or lineages) and nodes (points where a branch splits, i.e., speciation events). Branches may be terminal (tip, leaf, OTU) or internal (ancestor, internode); a root is a special branch that serves to indicate the time axis: the root is in the past and the tips are in the present. In this fully resolved, dichotomous tree, Riccia and Psilotum are each others’ closest relatives (‘sisters’), while Chara is more distantly related to both.
Evolution: Process and History